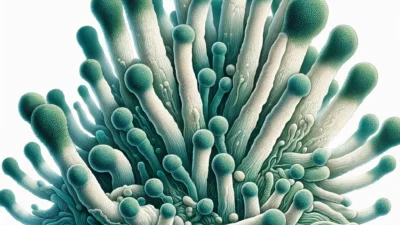
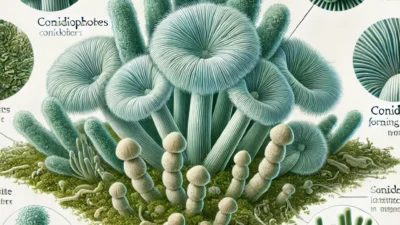
Fusarium species are known as mold fungi that are commonly found in soil and cause plant diseases.This group of fungi, which can cause serious damage to agricultural products, can also pose a threat to human health with some species.In this article, we will examine all the details that need to be known, from the scientific features of Fusarium species to their natural habitats and cultural importance.Scientific Name and Other Names Fusarium is a group of fungi that includes many different species belonging to the Fusarium genus.This name, derived from the Latin word “fusiform”, describes the spindle-shaped structure of the fungus’s spores.It is scientifically known for its species such as Fusarium oxysporum, Fusarium solani, and Fusarium graminearum.They are commonly known by names such as “agricultural pathogen” or “root rot fungus” because they commonly cause plant diseases, especially in agricultural areas.Regions Where It Occurs and Physical Characteristics Fusarium species are widely found throughout the world and have the ability to adapt to different climates.They can be found in soil, plant roots, dead organic matter and aquatic environments.Especially in hot and humid conditions, they can settle on plant roots, multiply rapidly and penetrate plant tissues.Physically, the microscopic structure of Fusarium fungi is quite distinct.Spores are generally spindle or elliptical in shape, and the color of the spore-producing structures may be white, pink or yellowish, depending on the species.Colony structures generally have a cottony appearance and can grow rapidly.Due to their widespread presence in the soil, they can directly come into contact with the root system of agricultural products, which paves the way for the occurrence of plant diseases.Growth Habitat and Reproduction Mode Fusarium species thrive in moist and nutrient-rich environments.They can be concentrated near plant roots, especially in agricultural lands.Reproduction rates vary depending on environmental conditions such as temperature, humidity and pH level.This fungus, which lives in the soil, can damage plant roots and prevent water and nutrient uptake, causing the plant to wilt and die.Fusarium fungi are capable of both asexual and sexual reproduction.In asexual reproduction, they produce spores called “macroconidium” and “microconidium”.These spores can be easily transported by wind or water and spread over large areas.In sexual reproduction, they form structures called “ascospores”.These modes of reproduction enable Fusarium species to become resistant to environmental conditions and spread rapidly in agricultural areas.Season and Harvest Time of Fusarium Species Fusarium species can survive in the soil throughout the year;However, warm and humid conditions are the most suitable periods for their reproduction.In spring and summer, especially during periods of abundant rainfall, the risk of Fusarium spreading in agricultural areas increases.Spores of the fungus may become active in the soil during crop harvest or irrigation.In regions where Fusarium-related diseases are common, it is of great importance to implement appropriate agricultural practices, taking seasonal changes into consideration.Fusarium Species and Their Agricultural Importance Fusarium species are pathogens that can cause serious losses in agricultural products.For example, Fusarium oxysporum causes root rot and wilt in many vegetable and fruit plants.This fungus enters the plant roots, damages the plant’s vascular system and prevents water and nutrient uptake, causing the plants to turn yellow, wilt and eventually die.On the other hand, species such as Fusarium graminearum cause the disease known as ear rot in grains. The mycotoxins produced by these species can pose serious health risks when contaminated with animal feed and human food.Measures such as developing seed varieties resistant to Fusarium diseases, performing crop rotation and using biological control methods in agricultural areas play a critical role in the fight against these fungi.Interesting Information About Fusarium Species
- Toxic Effects: Some Fusarium species produce poisonous substances called mycotoxins.These toxins may pose a risk to food safety by contaminating animal feed and human food.
- Plant Protection Studies: Biological control methods are being developed against Fusarium species in agriculture and studies on new plant varieties are being developed to reduce the effects of these fungi.
- Various Host Plants:Fusarium fungi can damage many different types of plants, including wheat, corn, tomatoes and potatoes.For this reason, they need to be carefully monitored in every agricultural area.
- Compatible with Tropical and Subtropical Areas: Fusarium is especially common in tropical and subtropical regions because it likes high temperature and humid environments.However, it can also cause diseases in temperate regions.
Frequently Asked Questions What is Fusarium?Fusarium is a type of mold fungus that can cause diseases in agricultural crops and is commonly found in soil.It specifically targets plant roots and damages their growth and development.How is Fusarium spread?Fusarium can spread through air, water or agricultural equipment by producing spores called conidia.These spores can reach plant roots and cause infection.What plants does Fusarium damage?Fusarium can cause diseases in many agricultural products such as wheat, barley, corn, tomatoes, potatoes and peppers.It is especially known for diseases such as root rot and ear rot.How to prevent Fusarium diseases?Crop rotation, biological control, using resistant plant varieties and ensuring proper drainage in agricultural lands are methods used to prevent the spread of Fusarium diseases.What are the effects of Fusarium on humans?Some species of Fusarium produce mycotoxins, and these toxins can harm human health when consumed with food.However, direct human infections are rare.In which season is Fusarium most common?Fusarium becomes more active in warm and humid conditions.Therefore, the risk of spread in agricultural areas increases in spring and summer.Fusarium species are an important group of fungi that pose serious threats to plant health in agricultural areas.Damage to plant roots by these fungi can lead to great losses in food production, while the toxins produced by some species may pose a risk to food safety.In order to ensure sustainable and efficient production in agriculture, it is of great importance to recognize Fusarium species and develop effective combat methods against them.In this article, we have presented comprehensive information about Fusarium, from its scientific features to its agricultural effects.Understanding Fusarium fungi and their impact on agriculture can help farmers cope with the challenges they face…