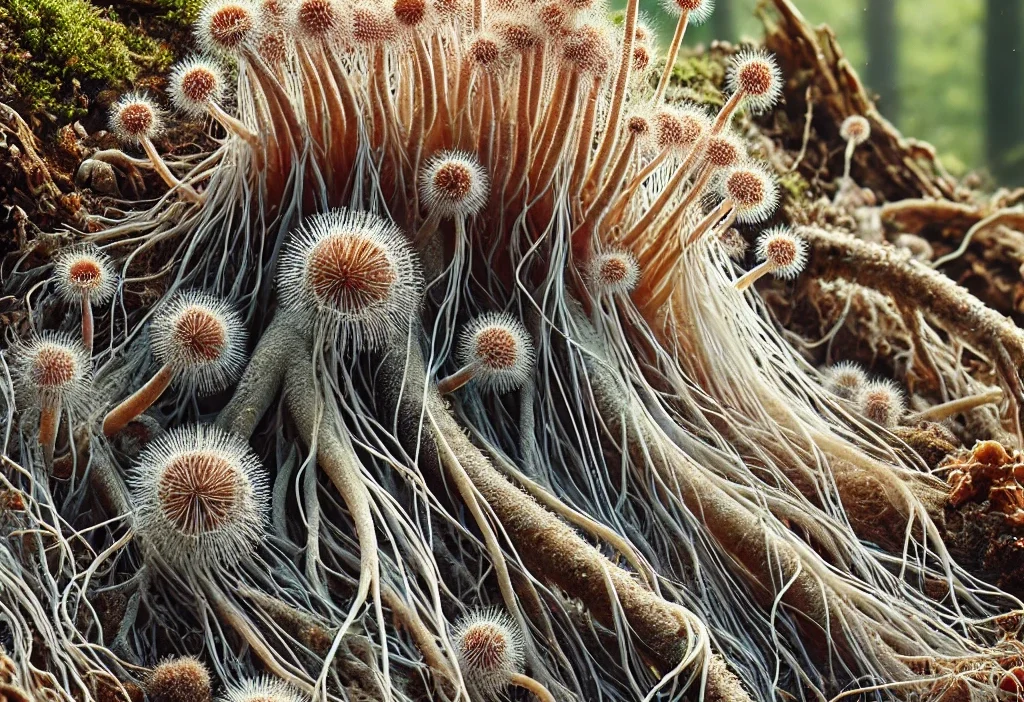
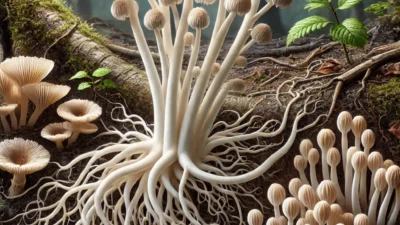
Ectendomycorrhizal fungi are a special group of fungi that establish symbiotic relationships with plant roots, both on the outer surface and in the inner cells.These fungi establish a deep symbiotic relationship with the plant, thanks to their hyphal structures that penetrate into the root cells and hyphal networks that spread over the root surface.These fungi, which combine some characteristics of both ectomycorrhizal fungi and endomycorrhizal fungi, play a great role in nature.Especially in forest ecosystems, they support plants to grow healthier by increasing their nutrient intake.Here’s everything you need to know about ectendomycorrhizal fungi!Scientific Name and Other Names of Ectendomycorrhizal Fungi These fungi, scientifically called Ectendomycorrhizal fungi, represent a special class of mycorrhizal fungi.This name comes from the structure of the fungi that both spreads to the outer surface of the roots (ecto-) and penetrates into the root cells (endo-).Thanks to these features, ectendomycorrhizal fungi exhibit both ectomycorrhizal and endomycorrhizal properties and are distinguished from other mycorrhizal fungi in these aspects.This type of fungus establishes a symbiotic relationship with plants, especially plants from the Pinaceae family and some shrub plant species.While ectendomycorrhizal fungi connect with the external environment by creating hyphal networks on the root surface of plants, they also play an active role in plant roots with their hyphae extending into the root cells.This two-way symbiosis increases the plant’s access to water and nutrients, making them more resilient to environmental conditions.Regions Where Ectendomycorrhizal Fungi Occur Ectendomycorrhizal fungi are widely found in forested areas in temperate climates and high altitude regions around the world.In forests where trees such as pine, fir and oak are dense, these fungi establish symbiotic relationships with the roots and contribute to the healthy functioning of the ecosystem.In addition to being widely seen in the forests of North America, Europe and Asia, they also live in the high-altitude forests of tropical regions.In Turkey, ectendomycorrhizal fungi are frequently found in pine forests in the Black Sea and Mediterranean Regions.The humid climate and rich vegetation of the Black Sea provide an ideal environment for the development of these fungi.They are widespread in the Mediterranean Region, especially thanks to the symbiotic relationships they establish with maquis vegetation and pine species.In these regions of Turkey, ectendomycorrhizal fungi contribute to the biodiversity of forest ecosystems and soil fertility.Physical Characteristics of Ectendomycorrhizal Fungi Ectendomycorrhizal fungi are microscopic fungi that form thin filamentous structures called hyphae.These hyphae spread over the outer surface of plant roots, forming a wide network, and also penetrate into the root cells.The fact that the hyphae extend into the root cells allows a close symbiotic relationship to be established between the plant and the fungus.Thanks to the hyphal structures they form within the root cells, water and nutrient exchange between the fungus and the plant takes place more effectively.The hyphal network (mantle) formed by ectendomycorrhizal fungi on the outer surface helps protect the roots against the external environment and facilitates the roots’ access to water.Thanks to these structures, plant roots become more resistant to environmental stress conditions.When the internal structure of hyphae is examined under a microscope, it is observed as branched and tightly connected structures to the cells.The spore structures of these fungi disperse in the soil and enable them to spread by establishing symbiotic relationships with new roots. Spores of ectenomycorrhizal fungi contribute to the nutrient cycle in nature, supporting the health of ecosystems.They survive in underforest ecosystems, among leaf litter and decaying woody materials.These fungi are found on the forest floor as they form tight symbiotic relationships with roots, facilitating plants’ access to water and nutrients.The periods when these fungi are most active are spring and autumn, when there is abundant rainfall.During these periods, soil moisture increases and ectendomycorrhizal fungi strengthen their symbiotic relationships with the roots.During the summer months, their activities may decrease due to drought;However, they become active again when the humidity level increases again.During the winter months, they continue their existence in the soil thanks to their structure that is resistant to low temperatures.The Role of Ectendomycorrhizal Fungi on the Ecosystem Ectendomycorrhizal fungi play an important role in the healthy functioning of forest ecosystems.These fungi, thanks to the relationships they establish with plant roots, enable plants to absorb water and mineral substances from the soil more efficiently.They play a critical role in transporting vital nutrients for plants, especially phosphorus and nitrogen, from the soil to the plant.The ability of ectendomycorrhizal fungi to improve soil structure and increase water retention capacity helps maintain the water balance of forests.Thanks to their hyphae structure, they regulate the movement of water in the soil by creating microscopic channels in the soil.This process facilitates plants’ access to water and helps them survive, even during periods of drought.In addition, these fungi accelerate the decomposition of organic matter, enrich the soil structure and contribute to the biodiversity of the ecosystem.Agricultural and Economic Importance of Ectendomycorrhizal Fungi Although Ectendomycorrhizal fungi are not used directly in agricultural production, they have an important role in protecting the health of forests and afforestation efforts.These fungi support the rapid growth of forest trees and their resistance to environmental stresses.Thanks to ectendomycorrhizal relationships, the root systems of young trees are strengthened and the healthy development of forests is ensured.In forest management and afforestation projects, the presence of ectendomycorrhizal fungi helps trees cope with environmental problems such as drought and soil deficiency.In addition, the natural fertilization effect provided by these mushrooms increases the fertility of the soil and reduces the need for chemical fertilizers.Thus, they provide important support for sustainable forest management and environmentally friendly practices.Interesting Information and Cultural Importance Ectendomycorrhizal fungi are an important subject of research on root symbiosis in the scientific world.The relationships of these fungi with plant roots have a major impact on plant growth and soil health.By examining the interactions of these fungi with their root systems, scientists have obtained important information about the sustainability of forest ecosystems.Culturally, local communities living closely with forests have long understood the role of these fungi in forest health.For the protection and sustainable management of forests, awareness of the benefits provided by ectendomycorrhizal fungi supports the long-term health of ecosystems.Ectendomycorrhizal fungi are an important group of fungi that support plants’ access to water and nutrients and ensure the healthy functioning of forest ecosystems.Thanks to their close relationships with plant roots, they protect the biodiversity of forests and increase the fertility of the soil.Frequently Asked Questions What are ectendomycorrhizal fungi?Ectendomycorrhizal fungi are a group of fungi that establish symbiotic relationships with plant roots both on the external surface and inside the root cells, supporting their water and nutrient uptake.Where are the regions where ectendomycorrhizal fungi are seen?These fungi are common in forested areas around the world, especially in pine and oak forests.They are frequently encountered in the Black Sea and Mediterranean regions of Turkey.What are the contributions of ectendomycorrhizal fungi to the ecosystem?These fungi improve soil structure, increase plant access to nutrients and support biodiversity.With which plants do ectendomycorrhizal fungi form a symbiotic relationship?It supports their growth by establishing a close symbiotic relationship with pine, fir, oak and other forest trees.How are these mushrooms used in agriculture?Although they do not have direct agricultural use, they have an important place with the benefits they provide in protecting the health of forests and afforestation efforts.Why are ectendomycorrhizal fungi important for forest health?Thanks to its close relationships with plant roots, it contributes to the healthy growth of forest trees and the preservation of the biological diversity of ecosystems…
Rhizopogon Species (Rhizopogon)
Rhizopogon species, are a group of fungi that belong to the phylum Basidiomycota and establish a tight ectomycorrhizal relationship with pine…